Last updated on December 4th, 2023
Are you tired of playing the keyword-guessing game when it comes to SEO?
Look no further than semantic SEO. This approach shifts the focus from cramming keywords into your content to creating meaningful, relevant content that answers the questions and addresses the intent of your target audience.
By understanding the relationships and connections between different words and phrases, search engines can better understand the context and meaning behind your website content, leading to higher visibility and more qualified traffic.
So, if you want to stay ahead of the competition and provide a better user experience for your audience, let’s explore the power of semantics in SEO and see how it can take your online presence to new heights.
Understanding Semantics in SEO
Semantics in SEO refers to the study of the meaning of words and phrases in the context of search engine optimization.
This includes understanding how search engines interpret the content on a website and how to use language and structure to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results.
By understanding semantics in SEO, you can improve your website’s ability to rank well in search engine results and ultimately drive more traffic.
How Semantics Impact Search Rankings
- Relevance: Semantics plays a crucial role in determining the relevance of a webpage to a user’s query. Search engines use natural language processing (NLP) to understand the meaning of the content on your webpage and match it with the user’s query. Websites that use relevant keywords and provide useful information will rank higher on search engine result pages (SERPs).
- Quality Content: Semantics helps search engines like Google understand the quality of the content on a webpage. Websites with well-written, informative, and in-depth content organized in a logical structure will be considered to have better quality content and will be ranked higher on SERPs.
- Quality Content: Semantics helps search engines like Google understand the quality of the content on a webpage. Websites with well-written, informative, and in-depth content organized in a logical structure will be considered to have better quality content and will be ranked higher on SERPs.
- Latent Semantic Indexing: Search engines use Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) to understand the relationships between words and phrases on a webpage. LSI helps search engines understand the meaning of a webpage by looking at the words used in the content and the context in which they are used.
- User Intent: Search engines also leverage semantics to understand the user’s intent behind a query. Websites that provide content tailored to the user’s intent will be considered more relevant and thus ranked higher in search results. By analyzing the user intent, you can optimize the content and structure to best match the user’s needs.
Examples of Semantic Keywords and Phrases
Semantically related keywords and phrases are groups of words that are related in meaning to a main keyword or phrase. They’re often used to provide additional context and information about the main keyword or phrase.
For example, if the main phrase is “organic food,” semantically related phrases could include “natural food,” “non-GMO food,” “pesticide-free food,” “locally sourced food,” “sustainable farming,” and so on.
Some other examples of semantically related keywords are:
- “running shoes” and “athletic shoes”
- “organic produce” and “natural food”
- “marathon training” and “long-distance running”
- “leaky faucet” and “plumbing repair”
- “smoothie recipe” and “healthy breakfast”
- “business plan” and “startup strategy”
Here are some examples of semantic phrases:
- “running shoes” and “best athletic shoes for running”
- “organic produce” and “non-GMO fresh fruits and vegetables”
- “marathon training” and “long-distance running preparation”
- “leaky faucet” and “DIY faucet repair guide”
- “smoothie recipe” and “smoothie ideas for a healthy lifestyle”
- “business plan” and “strategies for a successful startup”
You’re bound to wonder, has Google always been that semantic?
Definitely not. It had its own evolution—let’s learn about that in the next section.
Semantic SEO and Google Updates
Over the years, Google updates have focused on understanding the meaning behind a user’s query and providing more relevant results.
With each update, Google’s ability to understand natural language, context, and user intent has become more advanced. Hence, there’s no better time than now to leverage semantic SEO to rank better on SERPs.
Take a look at the evolution of semantics in SEO with these key Google updates:
- Hummingbird: In 2013, Google released the Hummingbird update, which was designed to better understand the meaning behind a user’s query rather than just matching keywords.
- RankBrain: In 2015, Google launched the RankBrain update. Thanks to machine learning technology, RankBrain improved how Google handled queries with natural language and long-tail keywords.
- BERT: In 2019, Google released the BERT update. It helped Google understand more complex queries and thus provide more relevant results.
- Passage-based indexing: In 2020, Google started to roll out passage-based indexing, a feature that allows Google to understand and index specific parts of a webpage instead of just the whole page. With this feature, Google can understand the relevance of specific sections of a webpage to a user’s query and return that passage to SERPs.
Now that you understand how semantic SEO has evolved over the years and how it impacts search rankings, it’s time to introduce you to key strategies.
6 Proven Semantic SEO Strategies for Success
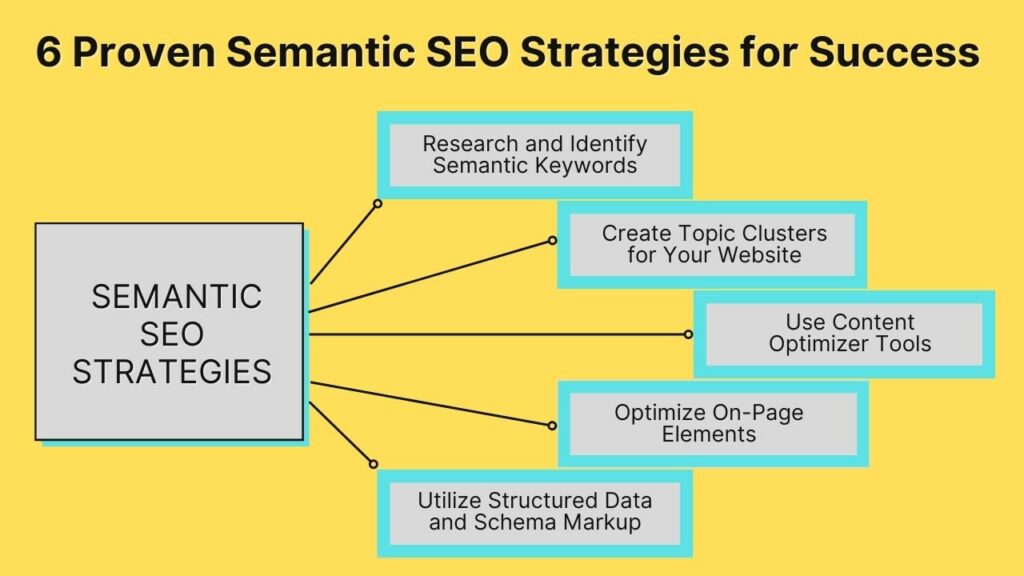
If you want to stay ahead of the competition and give your website the best chance to rank highly in search results, implementing semantic SEO strategies is a must.
Listed below are six such strategies:
1. Research and Identify Semantic Keywords
There are several ways to conduct semantic keyword research:
- Use keyword research tools: You can use keyword research tools, such as Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs, etc. These tools can provide data such as search volume, competition, and cost-per-click (CPC), which can help you prioritize which keywords to target.
- Analyze your competitors: Assess the content and keywords your competitors are using to identify opportunities for your own content.
- Check related searches: Use the “Searches related to” section at the bottom of the SERP to find other semantic keywords.
- Use LSI keywords: You can find LSI terms using tools such as LSIGraph, SEMrush, and Ahrefs.
- Look into the questions: Identify the questions that people are asking that are related to your main keyword. Use these questions as keywords to optimize your content. Tools like AnswerThePublic are designed for this purpose.
It’s important to find the right semantically related keywords that align with the intent of your target audience and incorporate them into your content organically.
2. Create Topic Clusters for Your Website
Topic clusters are groups of related content that all center around a specific main topic.
These clusters typically include one main piece of content, known as the “pillar” page, which provides an overview of the main topic, and several additional pieces of content, known as “cluster” pages, that dive deeper into subtopics related to the main topic.
The pillar page and the cluster pages are all linked together, with the pillar page linking to the cluster pages and the cluster pages linking back to the pillar page.
This creates a web of interconnected content that helps search engines understand the relationship between the different pages and thus improves your site’s semantic SEO signals.
Additionally, it makes the website structure more user-friendly, easy to navigate, and improves the user experience.

3. Use Content Optimizer Tools
First things first, what is content optimization?
It’s the process of improving the quality and relevance of the content on a website to make it more appealing to both users and search engines. This can include things like:
- Researching and incorporating relevant keywords
- Improving the content’s readability
- Enhancing the user experience through the use of images, videos, and other multimedia
- Optimizing meta tags and other on-page elements
- Creating high-quality and unique content that provides value to the audience
- Optimizing the website’s structure, URLs, and hierarchy
- Ensuring the website’s speed is optimal and mobile-friendly
Many different tools are available to help you optimize content.
Some popular examples include:
- Google Analytics: This is a free tool used to track website traffic and analyze user behavior. It can help you identify which pages are most popular and which pages might need to be optimized.
- Yoast SEO: This is a WordPress plugin that can help optimize website content for search engines. It provides an analysis of the content and suggests ways to improve it, such as by incorporating keywords and enhancing readability.
- Moz: This is a paid tool that can be used for keyword research, link building, and competitor analysis.
4. Optimize On-Page Elements
On-page optimization is a key element of semantic SEO, as it helps search engines understand the context of your content.
Some common on-page SEO techniques include:
- Keyword research: Identifying the keywords that people are searching for in relation to your content and using them strategically in your website’s metadata (title tags, meta descriptions), content, and URLs.
- Title tags and meta descriptions: Creating compelling title tags and meta descriptions that accurately reflect the content of your webpage and include keywords.
- Header tags (H1, H2, H3): Using header tags to organize your content and make it easy for search engines to understand the structure of your webpage.
- Content optimization: Creating high-quality, informative, and engaging content that satisfies the user’s intent and includes keywords organically.
- Internal linking: Linking to other relevant pages within your website to help search engines understand the hierarchy and structure of your site.
- Image optimization: Optimizing images by using descriptive file names and alt tags and compressing them to improve page loading speed.
- URL structure: Creating clear and concise URLs that include keywords and are easy to understand.
- Sitemap: Submitting a sitemap to search engines to make it easier for them to crawl and understand your website’s structure.
- Structured data: Using structured data to provide additional information about your website to search engines, such as product details, business information, and reviews.
- Mobile optimization: Optimizing your website for mobile devices to ensure that it loads quickly and is easy to navigate.
5. Utilize Structured Data and Schema Markup
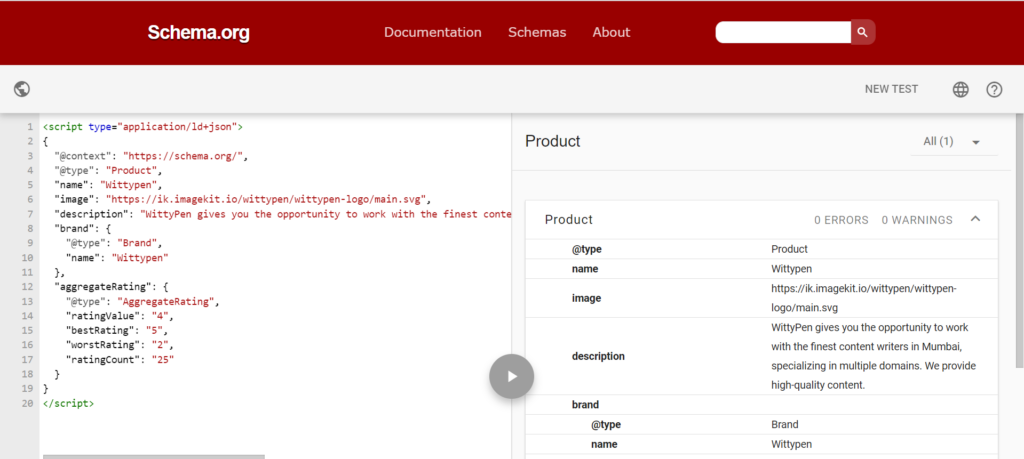
Schema markup, also known as structured data, is a way to annotate your website’s HTML code to help search engines better understand the content on your pages.
By providing additional information about the types of data on your pages, such as reviews, events, or products, you can help search engines more accurately understand the content of your website, which can help improve its visibility in search results.
There are several types of schema markup, including:
- Microdata: A format for embedding structured data within HTML documents.
- RDFa: A format for embedding structured data within HTML and XHTML documents.
- JSON-LD: A lightweight format for embedding structured data within JavaScript code.
- Microformats: A set of simple, open standards for marking up HTML to indicate the meaning of specific elements.
- Open Graph: A protocol for embedding structured data within the head section of a webpage, primarily used for social media sharing.
- Twitter Cards: A protocol for embedding structured data within the head section of a webpage, specifically for tweets.
Each of these types of schema markup serves a different purpose and is used by different search engines and platforms. It’s important to choose the right type of schema markup for your website based on your goals and the platforms you want to optimize for.
6. Respond to ‘People Also Ask’ Questions
Google now shows the “People Also Ask” box for 48.4% of search queries, as reported in a recent study conducted on 2.5 million search queries.
Incorporating People Also Ask (PAA) questions into your content can help improve semantic signals for your website. You can do so by:
- Researching PAA questions relevant to your topic and including answers to those questions in your content. This will signal to search engines that your content is relevant and informative for those specific questions.
- Using the PAA questions as inspiration for creating new content pieces. For example, if a PAA question is not directly answered in your article or blog post, you could create a new piece that specifically addresses that question.
- Using the language and phrases from the PAA questions in your content as semantic keywords.
Sematic SEO Tips for Optimizing Your Website
Now that you’re familiar with semantic SEO strategies, here are some tips to support them:
1. Create High-Quality, Relevant Content
Here are a few reasons why creating high-quality, relevant content is crucial for semantic SEO:
- High-quality content is more likely to be shared and linked to by other websites, which can help increase the authority and trustworthiness of your website.
- Relevant content is more likely to be found by search engines as it’s more likely to match the intent behind a user’s query.
- Google’s algorithm uses metrics such as click-through rate (CTR) and dwell time to understand user engagement on web pages. High-quality content can improve these metrics, which can help boost your search rankings.
2. Use Long-Tail Keywords and Natural Language
For effective semantic SEO, use long-tail keywords and natural language because:
- Long-tail keywords are both less competitive and more specific compared to short-tail keywords. They’re also more likely to match the intent behind a user’s query, which can help increase the relevance and visibility of your content in search results.
- Long-tail keywords can help you rank for a variety of related search queries, which can increase the visibility of your content and drive more traffic to your website.
- Using natural language in your content helps you improve the readability of your content and make it more user-friendly. This can help increase your site’s user engagement, which can positively impact your search rankings.
3. Incorporate LSI Keywords and Synonyms
LSI keywords and synonyms can help you avoid keyword stuffing, as you can use different terms to express the same concept, which can help you avoid penalization from search engines.
Moreover, LSI keywords and synonyms can help you rank for various related search queries, increasing your content’s visibility.
Here are a few examples of LSI keywords for the main keyword, “dog food”:
- Canine nutrition
- Dry dog food
- Wet dog food
- Grain-free dog food
- Premium dog food
- Natural dog food
- Homemade dog food
- Dog food brands
- Dog food ingredients
- Dog food recalls
- Dog food allergies
- Dog food storage
These LSI keywords help provide additional context and information related to the main keyword and can be used in content and meta tags to improve SEO content.
It’s important to note that LSI keywords are not always used just to improve SEO; they’re also used in NLP tasks and text classification.

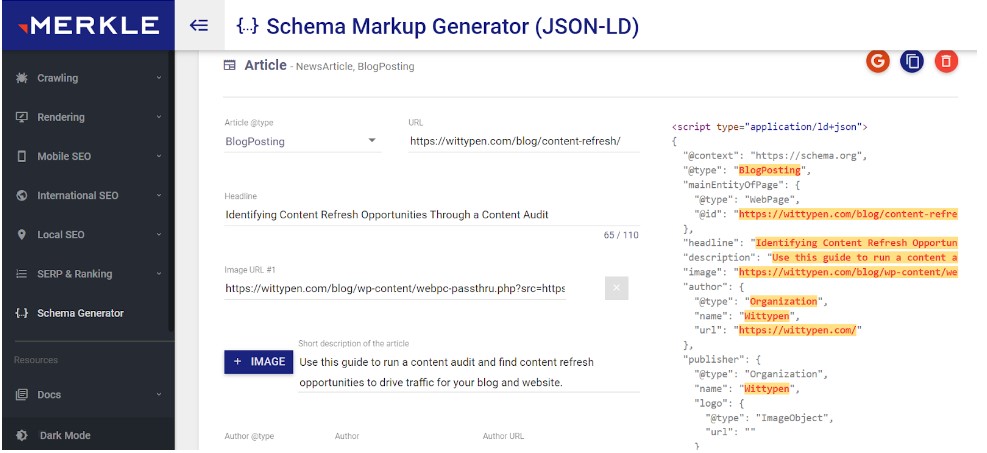
4. Create Schema Using ChatGPT and Online Schema Generator
Did you know you can generate schemas using an online schema generator and ChatGPT?
- An online schema generator is a tool that allows users to create a schema through a web-based interface. You can export the generated schema in a format that can be used to build the actual database.
- ChatGPT is a large language model developed by OpenAI. It’s based on the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture, which uses deep learning techniques to generate human-like text.

Apart from these tips, it’s crucial that you’re aware of the common semantic SEO mistakes to avoid, discussed next.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Semantic SEO
Semantics is an important part of any SEO strategy, but it can be tricky to get right. Here are some common mistakes to avoid to ensure your SEO efforts are successful –
1. Overstuffing Keywords
Keyword stuffing can do more harm than good and get you penalized by search engines. Doing so can not only hurt your search engine rankings but also make your content difficult to read and put off potential readers.
2. Neglecting User Experience and Relevance
It’s easy to overlook user experience and relevance when it comes to semantic SEO, but doing so can be a costly mistake. Neglecting these two can lead to poor website performance and decreased visibility in search engine rankings.
3. Ignoring the Importance of Structured Data
If you’re not using structured data, you’re missing out on one of the most powerful tools in the semantic SEO arsenal.
Structured data is essential for providing search engines with the information they need to understand your content and ensure your website is visible to the right people.
Conclusion
Semantic SEO is a great way of optimizing your website’s content to make it more easily understood by search engines. Using the right words and phrases and organizing your content in a way that helps search engines understand the meaning and context of your pages can reap you rich dividends.
For one, it can help your website rank higher in search results, making it more likely that people will find your site when searching for information related to your business or industry.
So, get going—implement the tips mentioned in this guide and regularly monitor your website’s performance to improve your website’s semantic SEO signals and help it rank higher on SERPs. Good luck!
FAQs
1. What is semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is a relatively new field of SEO that focuses on the meaning of search queries rather than the traditional keyword-based approach.
2. What is semantic search used for?
Search engines are constantly improving their algorithms to provide users with the most relevant results. A major part of this is semantic search, which takes into account the meaning of words and phrases to better understand the user’s intent.
3. Which is the most powerful SEO tool?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the most powerful SEO tool will vary depending on your specific needs and goals. Some say it’s Google’s Keyword Planner, while others swear by Moz’s Keyword Explorer.
4. How does semantic search work?
Semantic search looks beyond the literal meaning of words to find the underlying concepts they represent. It takes into account factors such as the relationships between words, synonyms, and the context in which the words are used.
5. How do I apply semantic SEO to different niches?
Semantic SEO can be applied to any niche, no matter how specific it may be. By researching the right keywords, analyzing the competition, and optimizing your content to be as relevant as possible, you can boost semantic SEO signals.